Addressing
Service Address
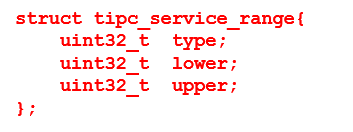
A Service address consists of two parts, assigned by the developer
- A Service Type number – typically hard-coded
- A Service Instance number – often calculated by user in run time

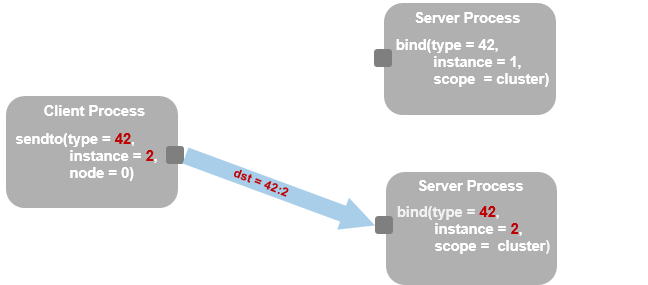
A service address is always qualified by a scope indicator
- Indicating lookup scope on the calling side node == 0 indicates cluster global lookup
- Indicating visibility scope on the binding side There are dedicated values for node local or cluster global visibility
node != 0 indicates that lookup should be performed only on that node
Service Address Binding
There are almost no restrictions on how to bind service addresses
- Different service addresses can be bound to same socket
- Same service address can be bound to different sockets
- Service address ranges can be bound to a socket
- Only one service address per socket in message bus mode
- This address type is also used for sending datagram and
communication group multicast

Location Transparency
A client doesn't need to know the location of the server
- Translation from service address to socket address is performed on-the-fly at the source node.
- There is a replica of the global binding table on each node for performing this translation.
- A sender can still indicate an explicit socket address when that is more practical,. e.g., when just responding to an incoming message.


